Summer of 1984 saw two major conventions happening in San Francisco. The Democrats were first, in July,  nominating Walter Mondale and Geraldine Ferraro for the ticket to run against Ronnie Reagan and George Bush the elder. Ferraro was the first female ever nominated for either President or Vice President, but, unfortunately it was a Republican world and they had no chance.
nominating Walter Mondale and Geraldine Ferraro for the ticket to run against Ronnie Reagan and George Bush the elder. Ferraro was the first female ever nominated for either President or Vice President, but, unfortunately it was a Republican world and they had no chance.
Later that summer, the world wide Iyengar community descended upon the Bay Area for the first (and only!) International Iyengar Yoga Convention. (Check out the hairy guy with Judith Lasater in the flyer!) During one of the question and answer sessions at the convention, Ramanand Patel asked B.K.S. Iyengar “what is ‘samyama in asana?”  As asana is the main focus of the Iyengar system, Ramanand’s question was designed to link posture with the meditative depths of Patanjali’s Yoga Sutras. We recorded the sessions on those old fashioned audio cassettes and I transcribed Iyengar’s answer word for word. Carol Cavanaugh and I edited it for punctuation and clarity and we published it as the lead article in the Iyengar Yoga Institute Review in October 1985.
As asana is the main focus of the Iyengar system, Ramanand’s question was designed to link posture with the meditative depths of Patanjali’s Yoga Sutras. We recorded the sessions on those old fashioned audio cassettes and I transcribed Iyengar’s answer word for word. Carol Cavanaugh and I edited it for punctuation and clarity and we published it as the lead article in the Iyengar Yoga Institute Review in October 1985.
I wish I could include the audio but I cannot find it. I listened to this so many times back in the 80’s his voice has burned into my brain cells. Even as I write this I hear his animated voice. After almost thirty years of my own enquiry I find his words ringing with amazing genius and depth. Words are not his strength, but he was inspired that day. As you read the transcript, recognize that the words were being spoken to an audience. This first part will include the article in full, as it first appeared in 1985 and I have also added some photos and charts that were not part of the original publication. In part two, coming soon, I will integrate my own commentary from the perspectives of neuro-science and my personal practice.
****************
Note: the following is a transcript of a discourse given by B.K.S. Iyengar  at the First International Iyengar Yoga Convention in August, 1984. Unfortunately, Mr. Iyengar’s first sentence or two were not recorded and the text begins in mid sentence. However, his ensuing discussion strongly implies that the missing segment introduces the five gross elements: fire, air, earth, water and ether. These elements compose part of the 25 principles of the Samkhya model of reality. Samkhya is the philosophical foundation of yoga. (See accompanying chart.)
at the First International Iyengar Yoga Convention in August, 1984. Unfortunately, Mr. Iyengar’s first sentence or two were not recorded and the text begins in mid sentence. However, his ensuing discussion strongly implies that the missing segment introduces the five gross elements: fire, air, earth, water and ether. These elements compose part of the 25 principles of the Samkhya model of reality. Samkhya is the philosophical foundation of yoga. (See accompanying chart.)
In this model, the evolution of consciousness proceeds from the most subtle aspects of mind to the grossest aspects of matter. Mr Iyengar describes the use of asana to retrace this process from the gross level back to pure consciousness. This requires the integration, the uniting of all the diverse aspects and elements into a single harmonious flowing consciousness.  The yogic term for this integrative process is Samyama. Samyama is the simultaneous practice of Dharana, Dhyana, and Samadhi, the last three limbs of Patanjali’s eight limbs of yoga and is described and discussed in Chapter Three of the Yoga Sutras. Kofi Busia’s succinct translation of the first few sutras of this chapter may be of use to the reader who is unfamiliar with these terms.
The yogic term for this integrative process is Samyama. Samyama is the simultaneous practice of Dharana, Dhyana, and Samadhi, the last three limbs of Patanjali’s eight limbs of yoga and is described and discussed in Chapter Three of the Yoga Sutras. Kofi Busia’s succinct translation of the first few sutras of this chapter may be of use to the reader who is unfamiliar with these terms.
“Concentration (Dharana) consists of keeping the attention centered in one area. Keeping the attention uninterrupted in that state is meditation (Dhyana.) Enlightenment (Samadhi) comes when the attention-keeping ability shines forth as an entity in its own right, quite separate from the means or objects first used to create or draw it forth. These three together are called insightful perception (Samyama). Achievement of it brings the very highest wisdom. It is used to discover higher and higher planes of wisdom.”
Mr. Iyengar’s discourse begins … “have peculiar qualities known as touch, form, sound, taste and smell. Our body is made up of these five elements with these five qualities of the elements; it comprises flesh, bones, bone marrow, blood, and so forth. Along with the five elements and five qualities of elements, each human has in their system to know five organs of action and five organs of perception. Legs, arms, excretory organs, generative organs and mouth are known as organs of action. Eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin are known as organs of perception. The elements are felt by action from the organs of action. There is tremendous communication between the organs of action and the organs of perception. While performing the asanas, the flesh, the marrow of the bones and the bones are organs of action, The skin, the feeling, the smell, the touch, the vibration, the movements are all connected to the organs of perception.
While performing the asanas, you and I, we have to very carefully observe that if the muscles are extended strongly, heavily, or with speed, the organs of perception cannot receive the action done by the fibers, by the cells, by the spindles, or the muscles. Hence they do not receive the actual functioning of the inner system which can only imprint on the organs of perception – the skin – to be felt later by the other parts: the eyes, the ears. So, when performing the asanas, one has to be very careful. The spindles of the physical elemental system (the fibers of the muscles) should act so as to not disturb the fibers of the organs of perception, 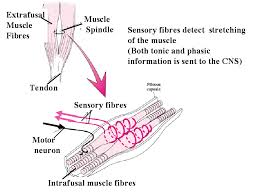 the inner layer of the skin. If they are not overstretched, naturally the organs of perception can receive the exact action done by the flesh. So when we are performing the asanas, we have to adjust in such a way that the fibers of the flesh do not protrude toward the skin more than what is essential.
the inner layer of the skin. If they are not overstretched, naturally the organs of perception can receive the exact action done by the flesh. So when we are performing the asanas, we have to adjust in such a way that the fibers of the flesh do not protrude toward the skin more than what is essential.
(In making contact between the movement and the organs of perception, all the elements become involved.) The power of intelligence you use to make contact is the element of air flowing in the system. They call it bio-energy, we call it prana. The will, the mind that you use, is the fire; the circulation which take place is connected to the element of water, and the mass of flesh within is nothing but the element of earth. And, while performing, as there is a pause between two sounds, a pause between two actions, as there is a space between two words, so also in the system there is an inner space, which is known as the element of ether.
When the asanas are performed, the power of intelligence, the element of air, should be spaced in such a way that the spindles of the organs of action, the flesh, allow the movement to come in contact with the spindles of the organs of perception, the inner layer of the skin. Then you understand the perfect balance of the presentation of that asana. If there is an overstretch, they are hard; you hit the organs of perception so strongly that they become insensitive. If there is an under-stretch there is no feeling; the organs of perception do not perceive the action. So when the organs of perception maintain their sensitivity, the fibers of the flesh, the organs of action have to be carefully handled inside, using the intelligence so that the fire, the mind, may not burn or move the fibers too fast or extinguish them.
And if you can do that way, than you know the contacting and balancing of the cells of the organs of perception through the cells of the organs of action; the ligaments, fibers and so forth. When they commune while performing, when you have understood the tremendous inner balance, without aggravating the organs of perception or of action, then you have mastered the asana. Only that asana! So the communication between the organs of perception and the organs of action should commune to the intelligence a certain rhythm and balance while performing. When that is performed, that asana is mastered. Sometimes we overstretch, sometimes we under-stretch, sometimes we use with will, sometimes we use the force of our body. These are known as imbalances in our presentations. When these are removed, the asana is perfect.
Now, there needs to be tremendous reflection because the elements have no reflection at all, they only act; but in acting they send a message to the organs of perception, triggering them to feel the essence of the action. In order to feel that, the organs of perception, which are connected to the brain, which is connected to the mind because the flesh is connected to the bone, and intelligence which is connected to the consciousness, must be intermingled to create the exact mixture, the exact blending of the fibers of the flesh with the fibers of the organs of perception. This requires tremendous repose, rethinking, reflection. Flesh acts, so it is a forward action from the flesh. Organs of perception should receive, should draw back. In order to draw back you have to create a pause, a space for the action, or the force of action which has been used, to be received by the organs of perception. That receiving movement is meditation in asana.
The acting movement requires skillful action. You have to create even more skillfulness to receive that skillful action with skillful organs of perception. That is why I said you have to communicate with each cell, with the air which is intelligence. So the intelligence acts as a bridge to bring the space, the ether, through vibration, sound, so that the organs of action and the organs of perception are brought very near,  without hitting each other. Each cell of the skin, while performing an asana, should exactly face level to the top layer of the flesh, or the cells of the flesh should be exactly facing the cell of the skin. One head of the spindle actually facing the other head of the spindle of the organs of perception. If that is done, that is known as integration, Samyama: that my cells of the body are completely one with the cells of the organs of perception. When the cells of action and the cells of perception have become one, the intelligence dissolves in those two, and makes these three vehicles of the consciousness as a single conscious movement in the entire body – this is samyama, or samadhi in that pose. I hope you understand – it is very difficult.”
without hitting each other. Each cell of the skin, while performing an asana, should exactly face level to the top layer of the flesh, or the cells of the flesh should be exactly facing the cell of the skin. One head of the spindle actually facing the other head of the spindle of the organs of perception. If that is done, that is known as integration, Samyama: that my cells of the body are completely one with the cells of the organs of perception. When the cells of action and the cells of perception have become one, the intelligence dissolves in those two, and makes these three vehicles of the consciousness as a single conscious movement in the entire body – this is samyama, or samadhi in that pose. I hope you understand – it is very difficult.”

